Simple Tips About How To Reduce Aggregate Demand

This can range from everyday.
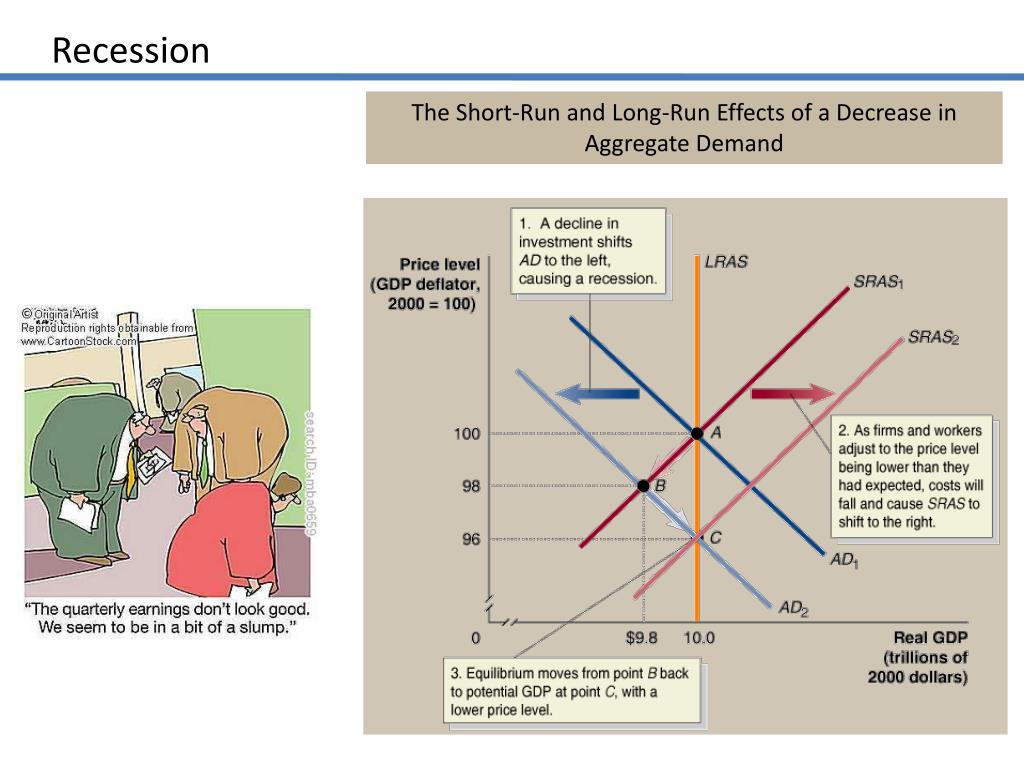
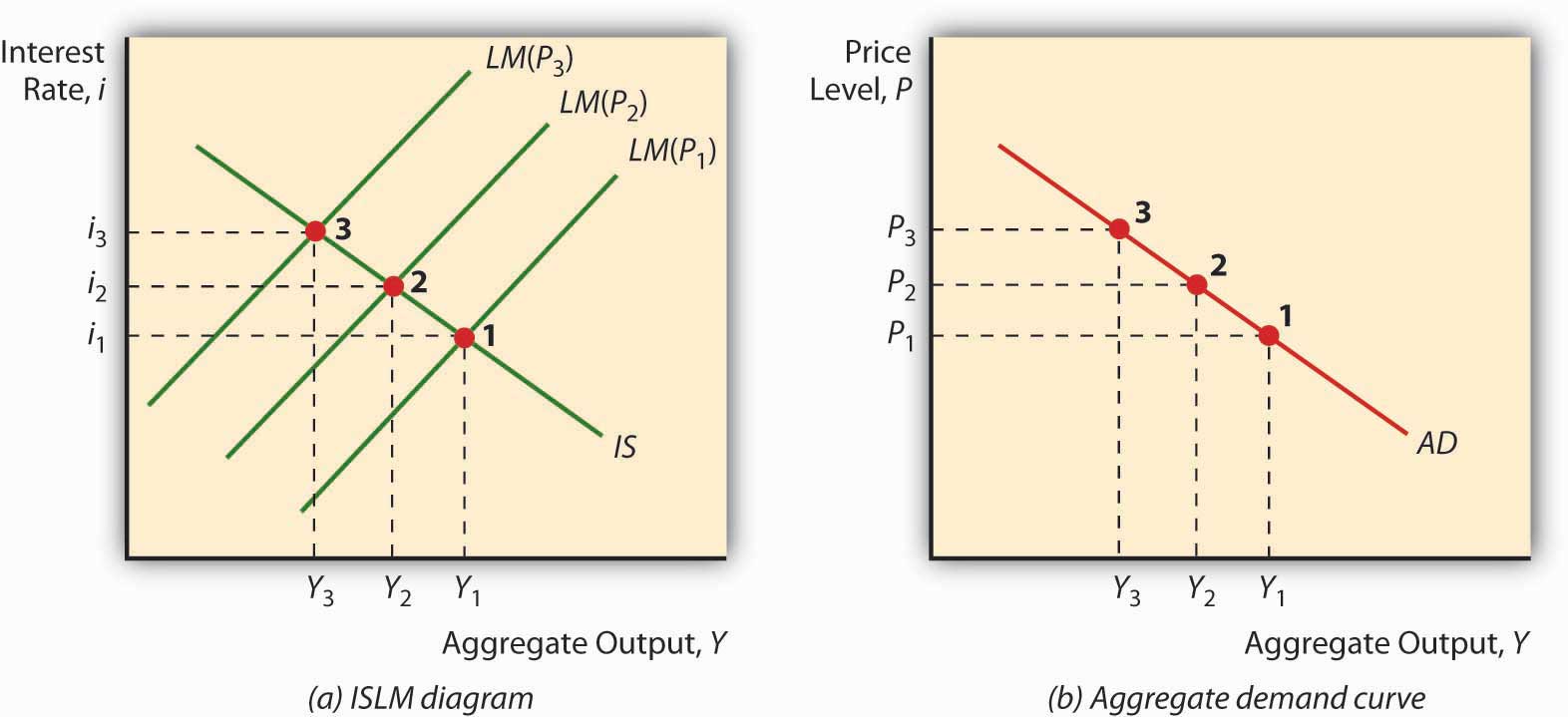
How to reduce aggregate demand. Both fiscal policy and monetary policy can impact aggregate demand because they can influence the factors used to calculate it: Consumption the largest component of aggregate demand (ad) is personal consumption of goods and services by households. Tight or contractionary monetary policy that leads to higher interest rates and a reduced quantity of loanable funds will reduce two components of aggregate demand.
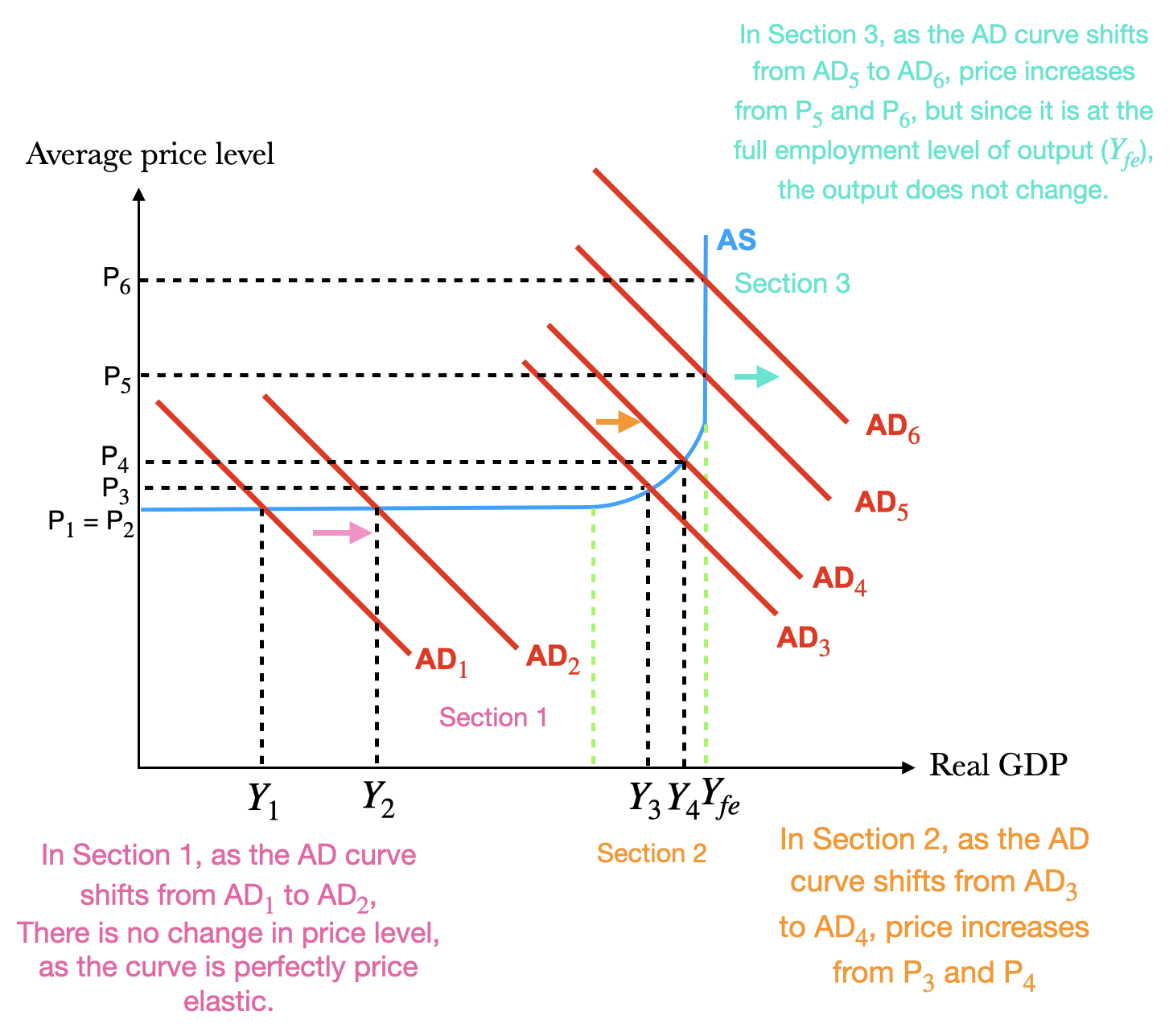
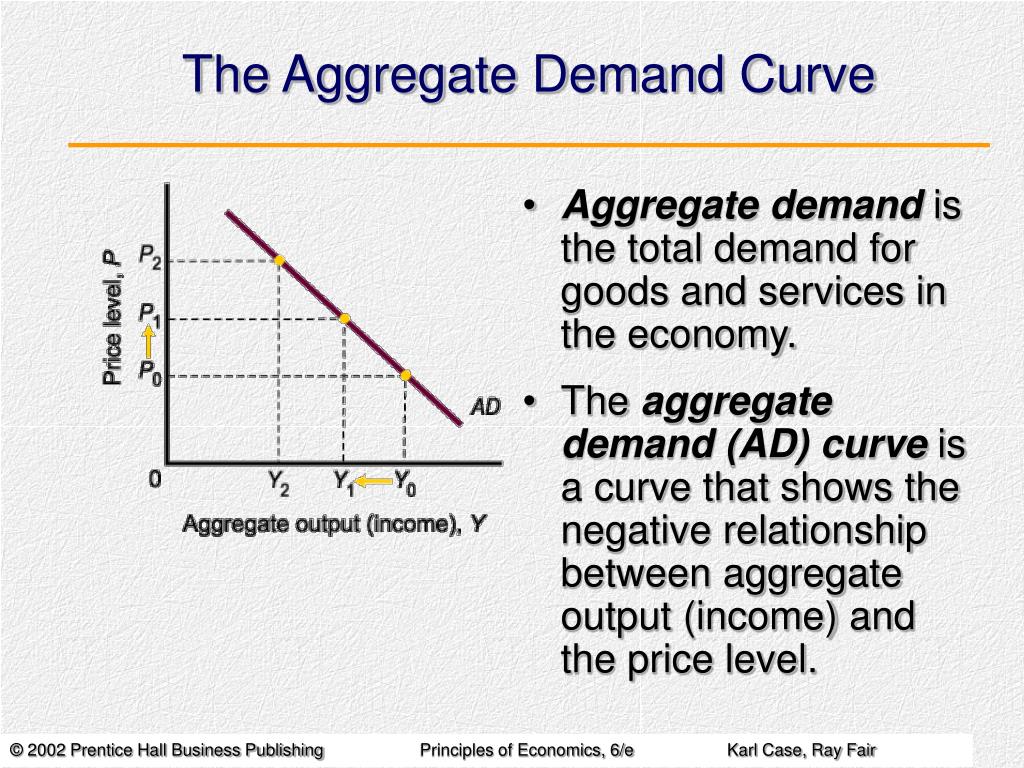
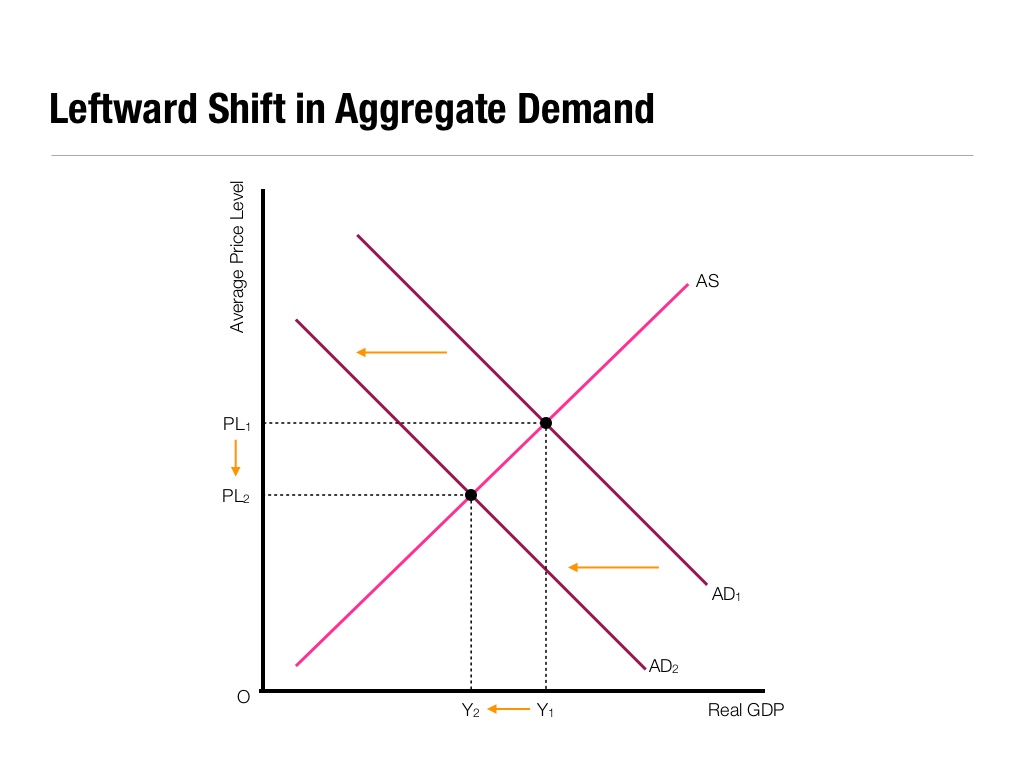
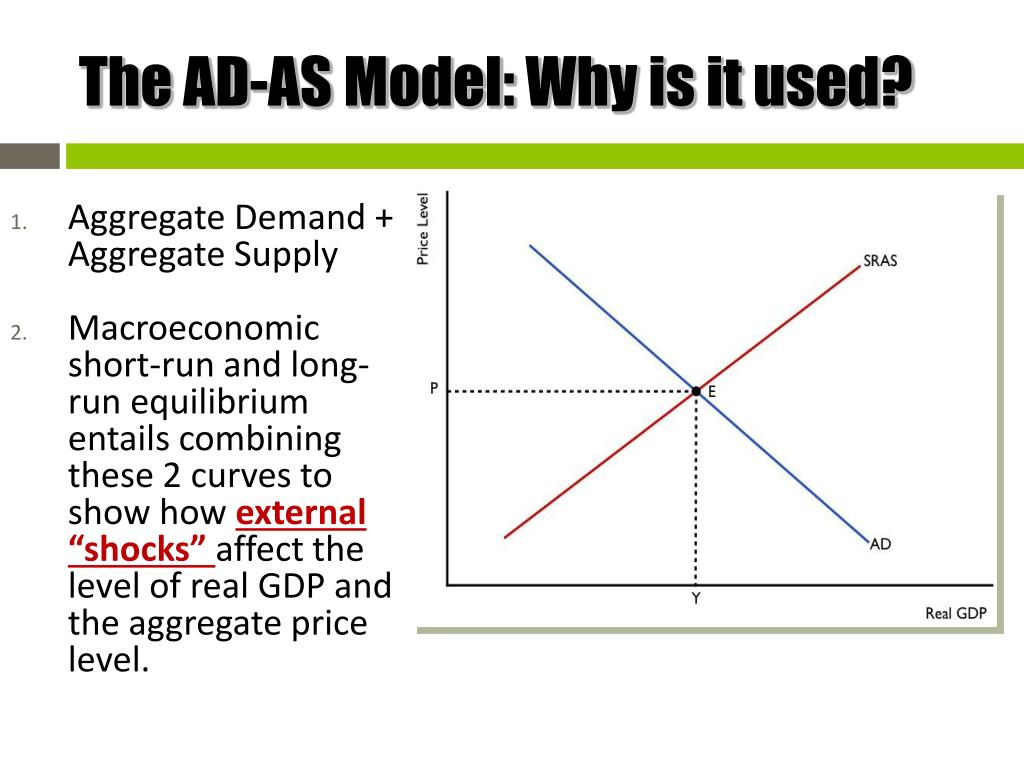
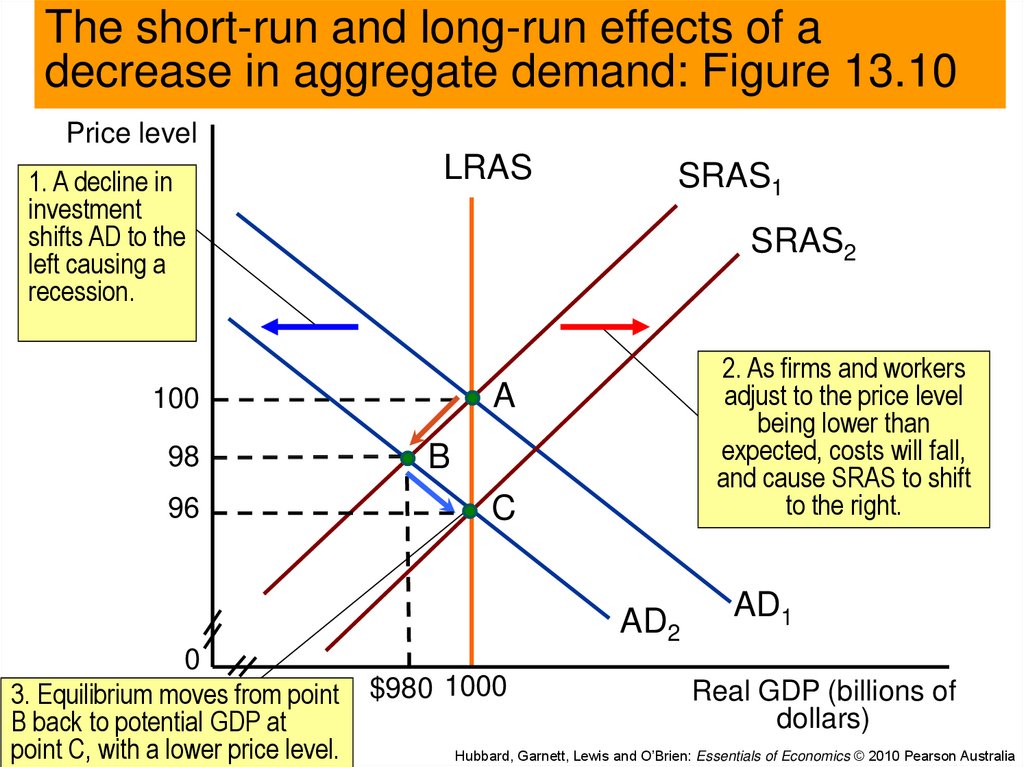
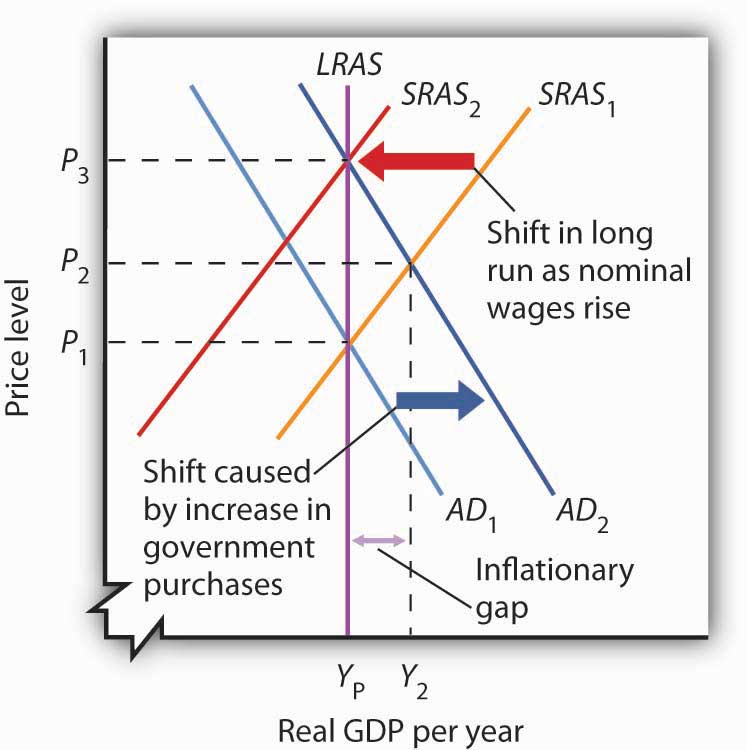
Conversely, a decrease in aggregate demand corresponds with a lower price level. Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for finished goods and services in an economy. A higher exchange rate tends to reduce net exports, reducing aggregate demand.
An increase in government purchases increases aggregate demand; A decrease in government purchases decreases aggregate demand. 1 answer sorted by:
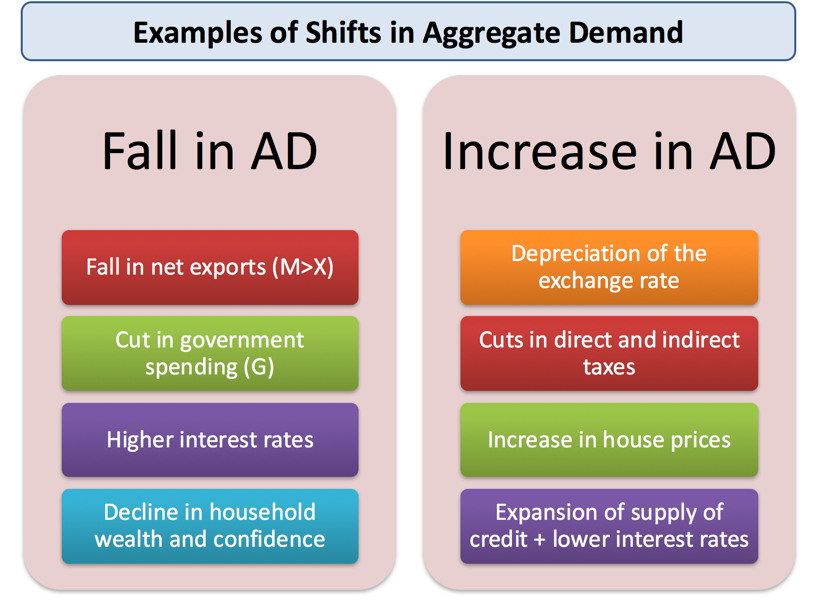
Reasons for a decrease in aggregate demand reasons for an increase in aggregate demand; A reduction shifts it to the left. Consumption can change for a number of.
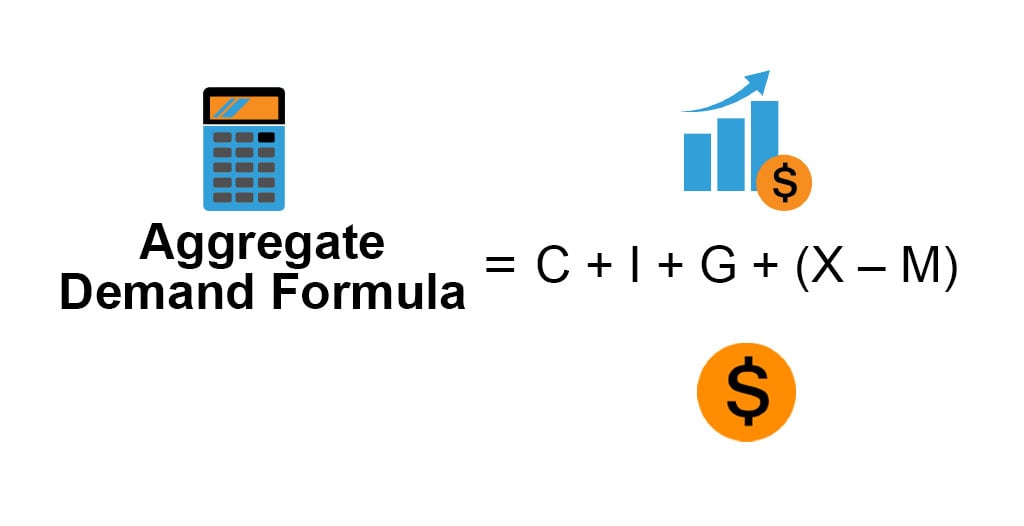
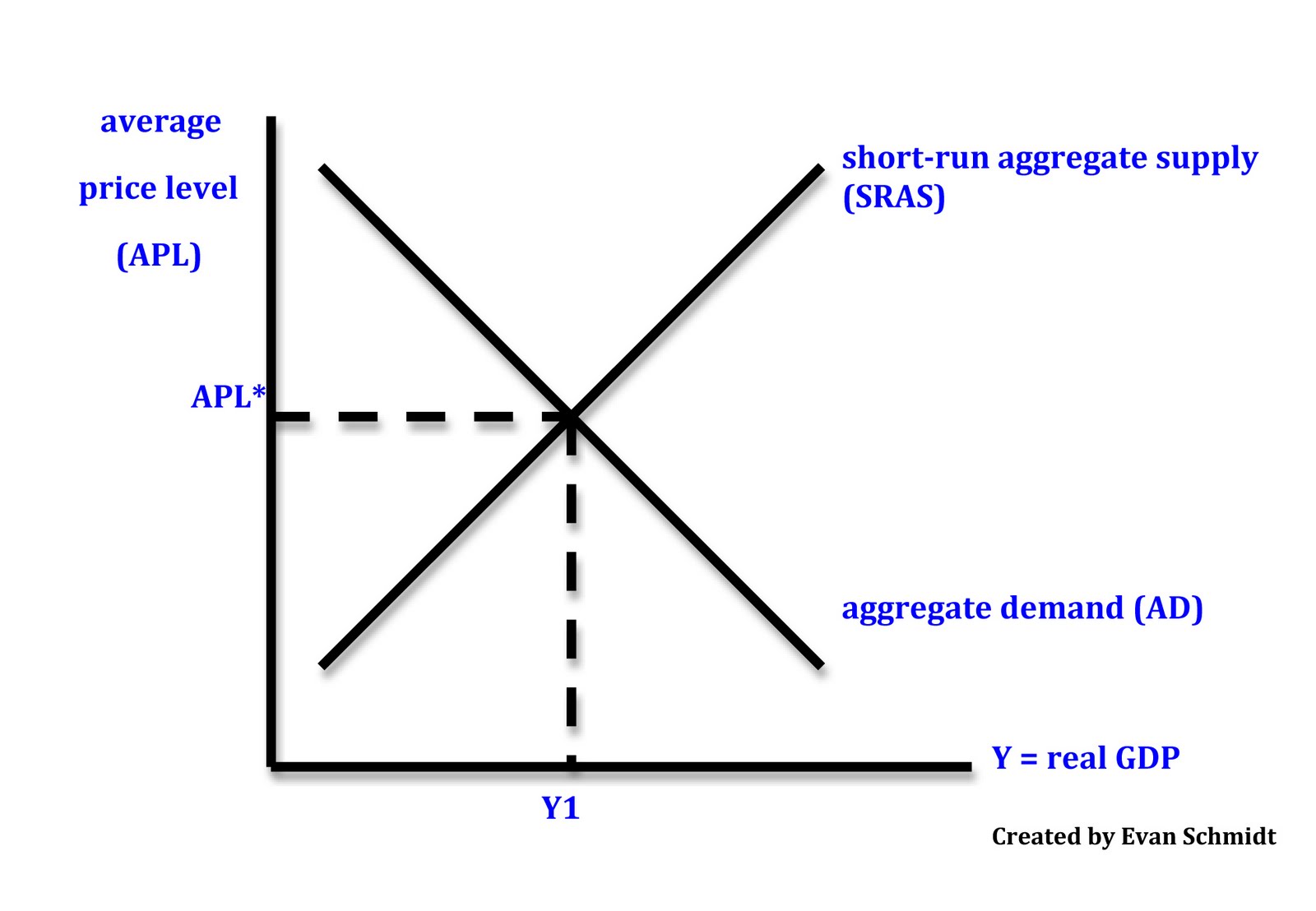
Consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports. Figure 24.8 shifts in aggregate demand (a) an increase in consumer confidence or business confidence can shift ad to the right, from ad 0 to ad 1. 2 aggregate demand is the total domestic demand for goods and services in an economy.
A lower exchange rate tends to increase net exports, increasing aggregate demand. Macroeconomics takes an overall view of the economy, which means that it needs to juggle many different concepts including the three macroeconomic goals of growth, low. A decrease in aggregate demand occurs when the components of.
Aggregate demand is the sum of four components: Cutting government spending could reduce. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports?
We learned earlier—in the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves article—that aggregate demand is made up of four components: