Unbelievable Tips About How To Cure A Stye In Your Eye

Clean your eyelids.
How to cure a stye in your eye. Use a warm compress using a warm compress is the most effective treatment for a stye. The warmth helps bring the pus to the surface and dissolve the pus and oil so the. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and rosacea, and.
Most styes are harmless to your eye and won't affect your ability to see clearly. Prescription antibiotic ointment to apply to your eyelid or antibiotic eye drops. For a stye that persists, your doctor may recommend treatments, such as:
Warm compresses help open your clogged eyelid gland. Prevention frequently asked questions a stye is caused by bacteria building up. Use a warm compress a warm compress is the most effective way to treat a stye.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotic eyedrops or a topical antibiotic cream to. A warm compress can help soften and break up the dirt and oil clogging the gland, as well as draw out infection. There are several potential causes, such as meibomian gland dysfunction or.
After washing your hands, soak a clean washcloth in very warm (but not hot) water and put it over the stye. For best results, apply the warm compress to the. When the stye is subjected to increased temperatures, it ruptures,.
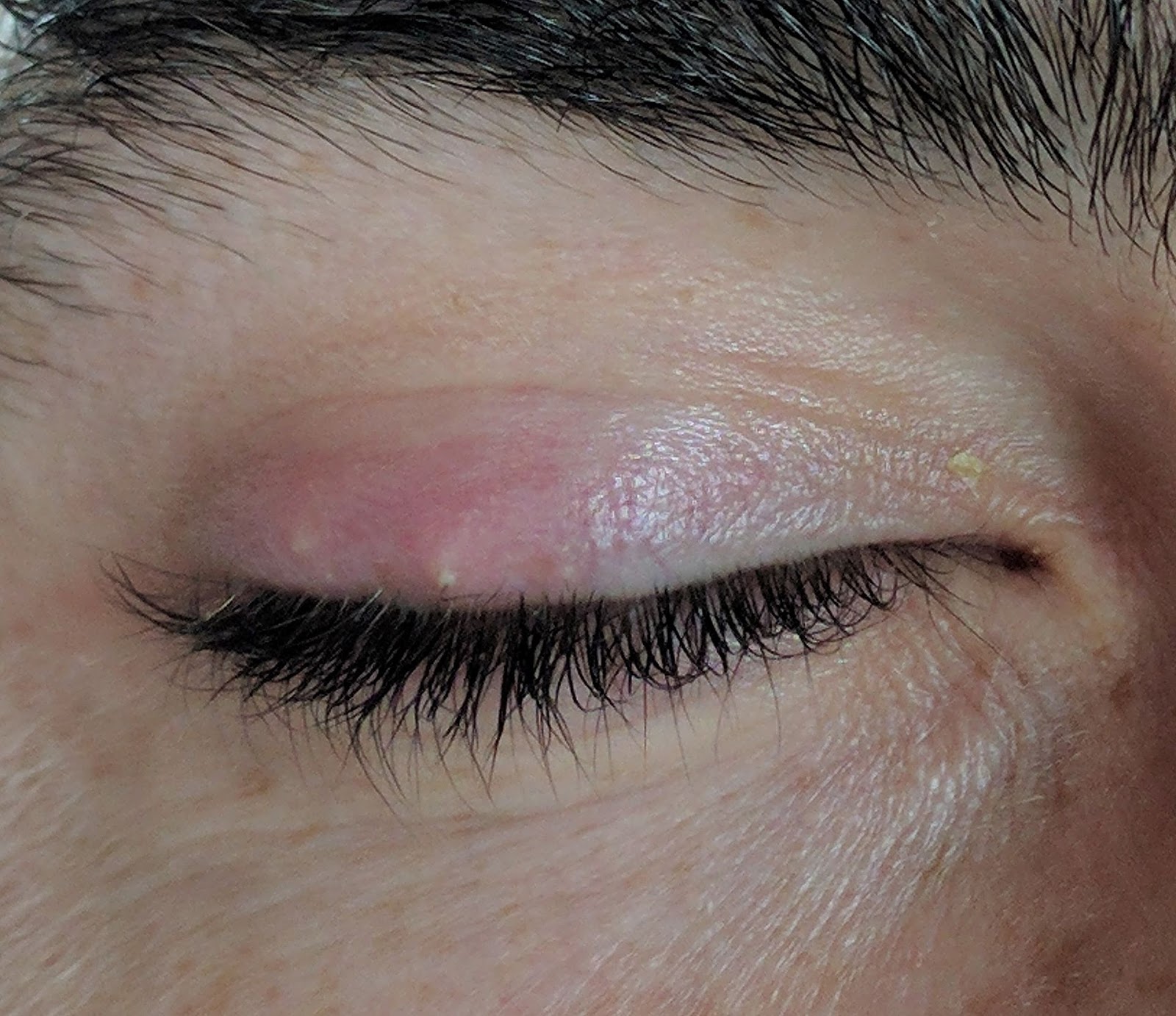
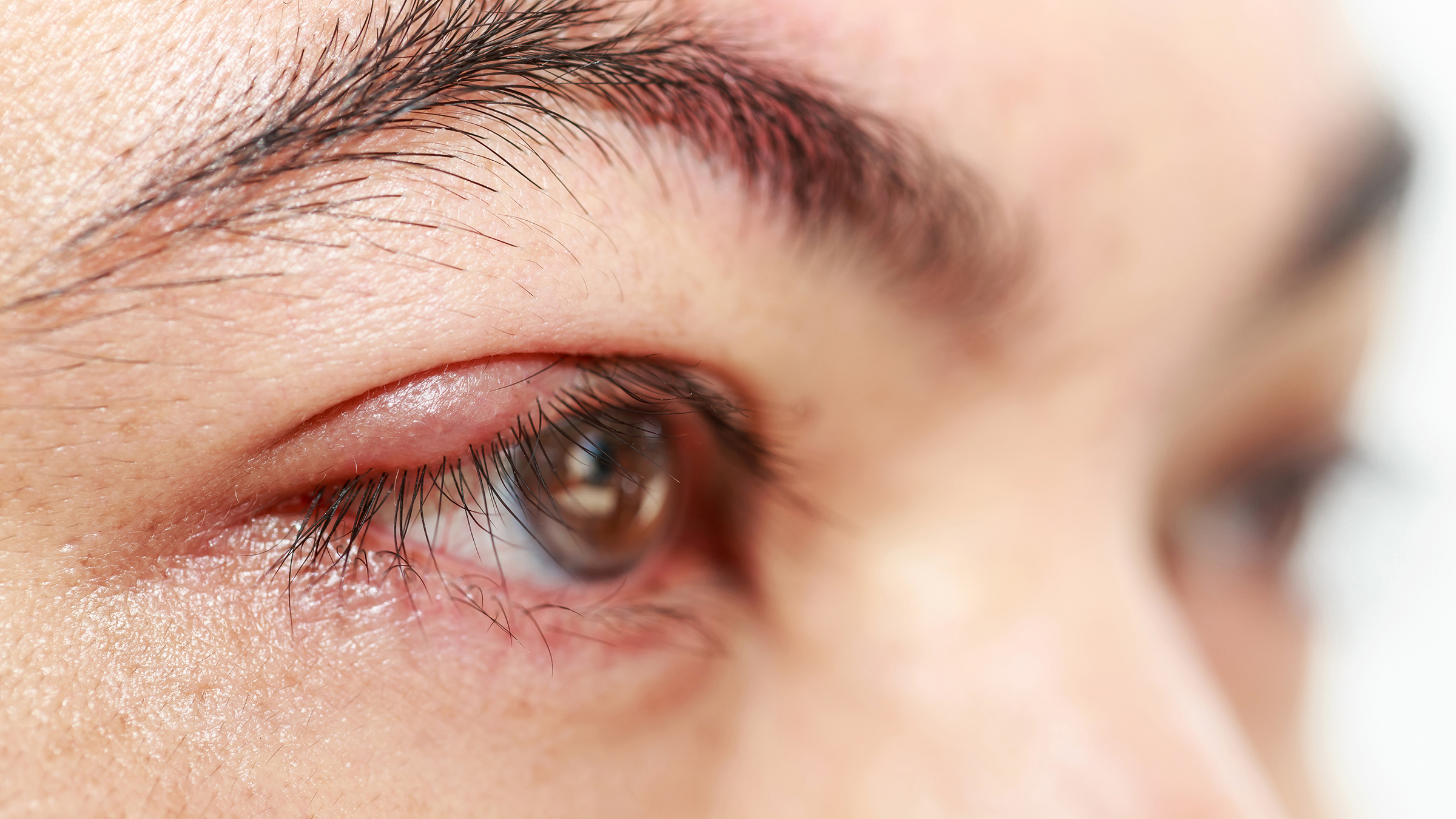
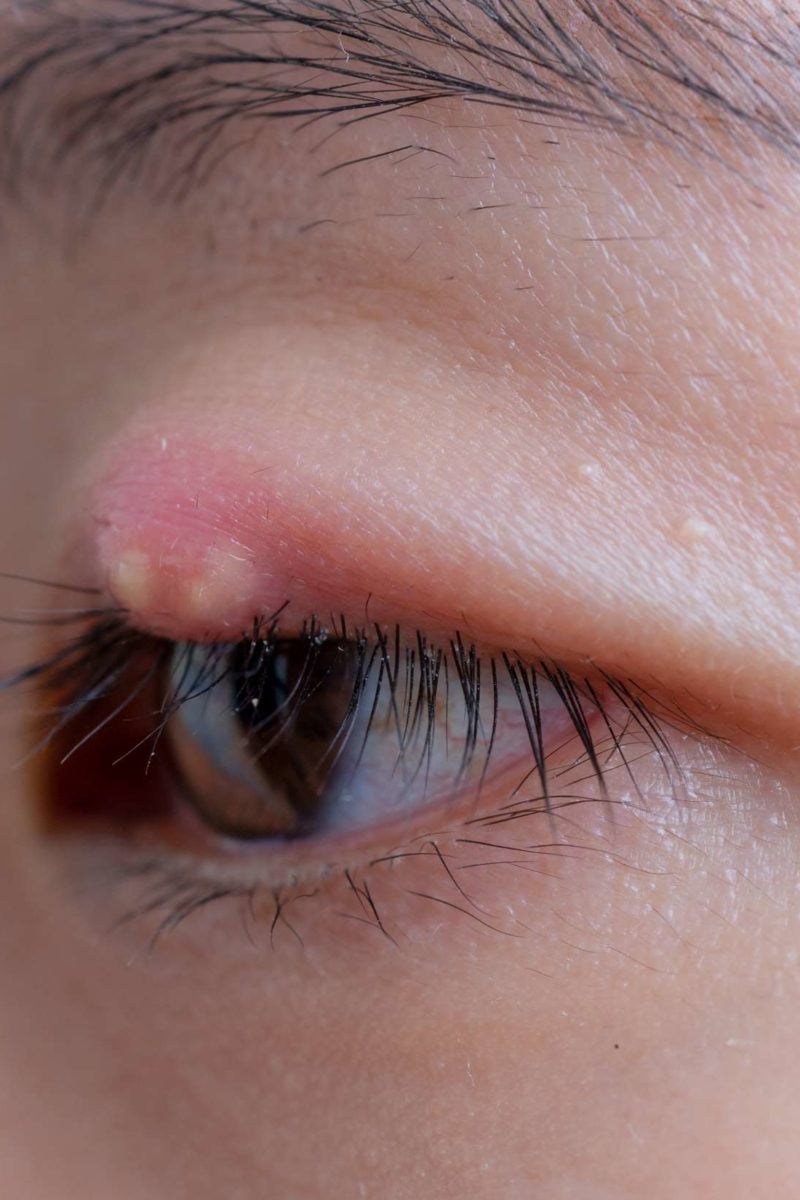
As it gets bigger, an. It can be itchy and may be more painful than styes outside the eyelid. Treatment faqs bottom line a stye is a lump on the eyelid caused by a bacterial infection.
You can do a few things to get rid of it faster: Gently massage the area with a clean finger to try to get the clogged gland to open and drain. The first thing you should do if you get a stye is cleanse your eyelids.
Right before bedtime, apply a warm compress or washcloth soaked in very warm water to your eyes for five to 10 minutes. This lets the debris, or gunk, stuck inside your stye flow out so your stye can start to heal. One of the main ways coconut oil helps treat styes is by lessening inflammation.
However, some styes may require professional medical care. It appears along the edge of the eyelid, due to infection in the eyelash follicle (where one of your eyelashes attaches to your eyelid).

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1214563916-f87daa6a288e467796df62c166b90303.jpg)